Alpha Lupi
| Alpha Lupi
| ||||
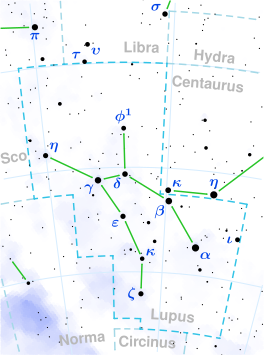
| ||||
| Die ligging van Alpha Lupi (in die rooi sirkel). | ||||
| Sterrebeeld | Wolf | |||
| Spektraaltipe | B1,5 III[1] | |||
| Soort | Reusester | |||
| Waarnemingsdata (Epog J2000) | ||||
| Regte klimming | 14h 41m 55.75579s[2] | |||
| Deklinasie | -47° 23′ 17.5155″[2] | |||
| Skynmagnitude (m) | 2,30[3] (2,29-2,34[4]) | |||
| Absolute magnitude (M) | -4,3[5] | |||
| B-V-kleurindeks | -0,20[3] | |||
| U-B-kleurindeks | -0,88[3] | |||
| Besonderhede | ||||
| Massa (M☉) | 10,1 ± 1,0[6] | |||
| Ligsterkte (L☉) | 25 000[5] | |||
| Ouderdom (jaar) | 16-20 miljoen[7] | |||
| Temperatuur (K) | 21 820 ± 2 160[8] | |||
| Rotasiespoed (km/s) | 16[7] | |||
| Metaalinhoud [Fe/H] | 0,04[9] | |||
| Eienskappe | ||||
| Veranderlikheid | Beta Cephei[4] | |||
| Ander name | ||||
| CD-46° 9501, FK5 541, HD 129056, HIP 71860, HR 5469, SAO 225128[10] | ||||
| ||||
Alpha Lupi (afgekort as α Lup) is die helderste ster in die suidelike sterrebeeld Wolf (Lupus). Dit het ’n skynbare magnitude van 2,3,[3] wat beteken dit is met die blote oog sigbaar. Volgens parallaksmetings[11] is die ster sowat 460 ligjare van die Son af.[2] Dit is die naaste ster wat amper as ’n supernova gaan ontplof.[12]
Eienskappe[wysig | wysig bron]
Alpha Lupi is ’n reusester met ’n sterreklassifikasie van B1,5 III.[1] Sy massa is sowat 10 keer dié van die Son,[6] maar sy ligsterkte is 25 000 keer die Son s’n.[5] Sy effektiewe temperatuur is 21 820 K[8] en dit het dus die blouwit kleur van ’n B-tipe ster. In 1956 het Bernard Pagel en sy kollegas ontdek dit is ’n Beta Cephei-veranderlike,[13] wat beteken sy ligsterkte wissel van tyd tot tyd vanweë pulse in die atmosfeer. Die wisselingsperiode is 0,29585 dae,[9] of net meer as sewe uur, ses minute. Die ligsterkte wissel met sowat 0,05, of 5% van die totale ligsterkte. ’n Ster van die 14de magnitude sowat 26 boogsekondes van Alpha Lupi af word in dubbelsterkatalogusse as ’n metgesel aangedui.[14]
Alpha Lupi is ’n eiebeweginglid van die Bo-Centaurus-Lupus-subgroep van die Scorpius-Centaurus-assosiasie (’n OB-assosiasie), die naaste groep swaar sterre aan die Son wat saam deur die ruimte beweeg.[5] Die assosiasie is sowat 16-20 miljoen jaar oud en is ook die bron van die borrel warm gas waarin die Son geleë is, bekend as die Plaaslike Borrel.[7]
Verwysings[wysig | wysig bron]
- ↑ 1,0 1,1 Hiltner, W. A.; Garrison, R. F.; Schild, R. E. (Julie 1969), "MK Spectral Types for Bright Southern OB Stars", Astrophysical Journal 157: 313–326, doi:10.1086/150069, Bibcode: 1969ApJ...157..313H
- ↑ 2,0 2,1 2,2 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 3,2 3,3 Johnson, H. L. et al. (1966), "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars", Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory 4 (99): 99, Bibcode: 1966CoLPL...4...99J
- ↑ 4,0 4,1 Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007–2013)". VizieR Aanlyn datakatalogus: B/GCVS. Oorspronklik gepubliseer in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1: 02025. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 5,0 5,1 5,2 5,3 de Geus, E. J.; de Zeeuw, P. T.; Lub, J. (Junie 1989), "Physical parameters of stars in the Scorpio-Centaurus OB association", Astronomy and Astrophysics 216 (1–2): 44–61, Bibcode: 1989A&A...216...44D
- ↑ 6,0 6,1 Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (Januarie 2011), "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 410 (1): 190–200, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x, Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T
- ↑ 7,0 7,1 7,2 Jilinski, E. (March 2006), "Radial velocity measurements of B stars in the Scorpius-Centaurus association", Astronomy and Astrophysics 448 (3): 1001–1006, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041614, Bibcode: 2006A&A...448.1001J
- ↑ 8,0 8,1 Sokolov, N. A. (Mei 1995), "The determination of T_eff_ of B, A and F main sequence stars from the continuum between 3200 A and 3600 A", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement 110: 553–564, Bibcode: 1995A&AS..110..553S
- ↑ 9,0 9,1 Daszyńska-Daszkiewicz, J.; Niemczura, E. (April 2005), "Metallicity of mono- and multiperiodic β Cephei stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics 433 (3): 1031–1035, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20040397, Bibcode: 2005A&A...433.1031D
- ↑ "V* alf Lup -- Variable Star of beta Cep type", SIMBAD (Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg), http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=V*+alf+Lup, besoek op 2009-10-26
- ↑ Perryman, M. A. C. et al. (April 1997), "The HIPPARCOS Catalogue", Astronomy & Astrophysics 323: L49–L52, Bibcode: 1997A&A...323L..49P
- ↑ Firestone, R. B. (Julie 2014), "Observation of 23 Supernovae That Exploded <300 pc from Earth during the past 300 kyr", The Astrophysical Journal 789 (1): 11, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/789/1/29, 29, Bibcode: 2014ApJ...789...29F.
- ↑ Pagel, B. E. J. (1956), "Results of a search for bright β Cephei variables in the southern sky", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 116: 10–24, doi:10.1093/mnras/116.1.10, Bibcode: 1956MNRAS.116...10P
- ↑ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal. 122 (6): 3466. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M. doi:10.1086/323920.
Eksterne skakels[wysig | wysig bron]
 Hierdie artikel is vertaal uit die Engelse Wikipedia
Hierdie artikel is vertaal uit die Engelse Wikipedia
