Antimoon(V)oksied
Voorkoms
|
Algemeen | |
|---|---|
| Naam | Antimoon(V)oksied |
 | |
| Chemiese formule | Sb2O5 |
| Molêre massa | 323,52 [g/mol][1] |
| CAS-nommer | 1314-60-9[1] |
| Voorkoms | geel vastestof[1] |
| Reuk | Reukloos[2] |
| Fasegedrag | |
| Selkonstantes | a=1455; b=468,2; c=2289pm; β 90°[3] |
| Ruimtegroep | C2/c |
| Nommer | 15 |
| Smeltpunt | 380 °C[2] |
| Kookpunt | |
| Digtheid | 3,78 [g/cm3] |
| Oplosbaarheid | Sleg oplosbaar[2] |
|
Suur-basis eienskappe | |
| pKa | |
|
Veiligheid | |
| Flitspunt | onbrandbaar |
| LD50 | 978 [mg/kg] (muis; interperitoneaal)[1] |
|
Tensy anders vermeld is alle data vir standaardtemperatuur en -druk toestande. | |
| Portaal | |
Antimoon(V)oksied is 'n verbinding van antimoon in sy hoogste oksidasietoestand (5+) met suurstof.
Die stof kan verkry word deur antimoon(III)oksied in 'n korund smeltkroes onder suurstof teen 700 °C te verhit.[3]
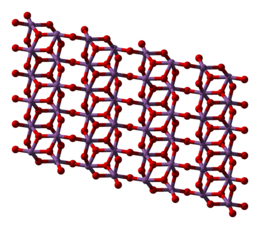
Kristalstruktuur
[wysig | wysig bron]Antimoon(V)oksied kristalliseer in die monokliniese B-Nb2O5-struktuur. In teenstelling tot die struktuur van As2O5 is alle katione in oktaëdriese omringing. Die antimoon-suurstof-afstande wissel van 191 tot 209pm. Die struktuur is verwant aan rutiel s'n. 'Lae' met rutielstruktuur is deur oktaëdriese hoeke verbind. [3]
Verwysings
[wysig | wysig bron]- ↑ 1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3 "Antimony pentoxide" (in Engels). PubChem NIH.
- ↑ 2,0 2,1 2,2 2,3 "Antimony Oxide Sb2O5". ESPI metal.
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 3,2 Jansen, M. (1978). "Crystal Structure of Sb2O5". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 17: 137–137. doi:10.1002/anie.197801371.
